
They are also used to treat less common conditions such as long QT syndrome and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Beta-blockers, as a class of medications, are essential drugs and are first-line treatments in many acute and chronic conditions.īeta-blockers are indicated and have FDA approval for the treatment of tachycardia, hypertension, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, essential tremor, aortic dissection, portal hypertension, glaucoma, migraine prophylaxis, and other conditions.
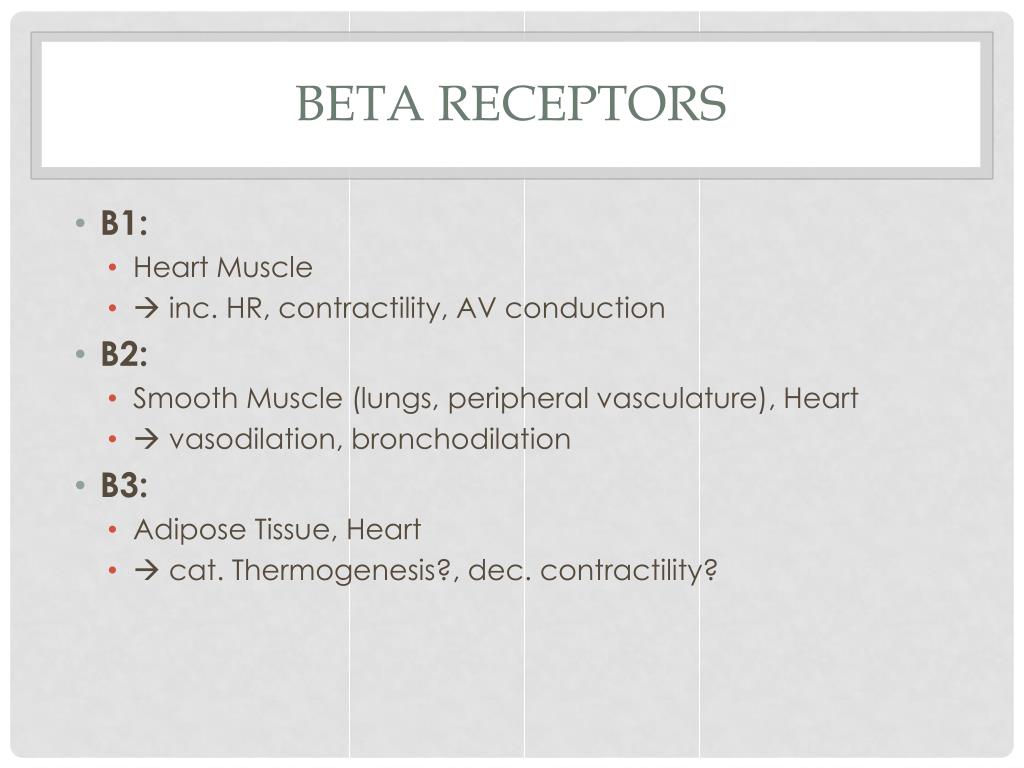
Blockade of these receptors by beta-blocking medicines is used to treat a broad range of illnesses. Beta-3 receptors induce the breakdown of fat cells and are less clinically relevant at present. Beta-2 receptors, with their diverse location in many organ systems, control various aspects of metabolic activity and induce smooth muscle relaxation. Beta-1 receptors located primarily in the heart mediate cardiac activity.

īeta receptors exist in three distinct forms: beta-1 (B1), beta-2 (B2), and beta-3 (B3). Outline the importance of improving care coordination among the interprofessional team to improve outcomes for patients using beta-blockers for indicated conditions.īeta-blockers, as a class of drugs, are primarily used to treat cardiovascular diseases and other conditions.Review the adverse events, contraindications, toxicities, and interactions of beta-blockers.Identify the indications for beta-blocker therapy.Summarize the mechanism of action of the beta-blocker class of medications, including the difference between selective and non-selective agents.This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, safe administration, adverse effects, contraindications, toxicology, and monitoring of the broad array of physiological possibilities when using beta-blockers in the clinical setting. Beta-blockers are indicated and have FDA approval for the treatment of tachycardia, hypertension, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, essential tremor, aortic dissection, portal hypertension, glaucoma, migraine prophylaxis, and other conditions. Beta-blockers, as a class of drugs, are primarily used to treat cardiovascular diseases and other conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
